
A development methodology determines how the actual tasks of a project are organized and acted on. Organizations often get stuck when deciding on which development methodology to choose.
Agile methodology introduces early delivery, predictable cost, high customer satisfaction, ease of new requirements, and many more. Among all the agile variations, Scrum is by far the most popular and widely adopted Agile methodology.
According to research, 94% of respondents use Scrum in their agile approach. The Scrum process helps companies improve the quality of products according to the changing requirements with a significant rise in productivity.
However, if you are a beginner, Scrum can be a difficult concept to grasp.
In this article, we’re covering all the essential aspects that you need to know about Scrum Framework.
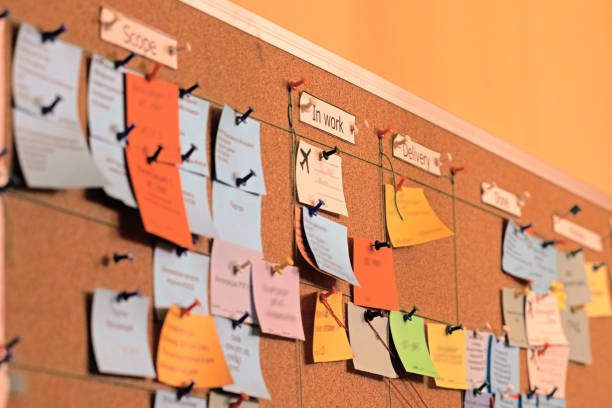
Scrum is a lightweight framework used to deliver complex innovative products and services that truly delight customers. It works by breaking down large products and services into small pieces that a cross-functional team can complete in a short time frame.
You can think of it as a collection of roles, events, artifacts used in combination to create iterative work products.
In Scrum, you don’t work in separate groups but you walk as one dedicated team. Instead of working on a project with distant deadlines, you constantly deliver functioning products throughout the cycle.
You don’t use final evaluation but you receive continuous feedback from your customers and improvise your product.
So, Scrum is a flexible way of working in the rapidly changing world.
To learn about the history of Scrum, we have to go back to the year 1986. In that year, two management experts Takeuchi and Nonaka, introduced the term Scrum.
They published a study in the Harvard business review, which explained that small cross-functional teams produce the best results. They borrowed the name from the game of rugby.
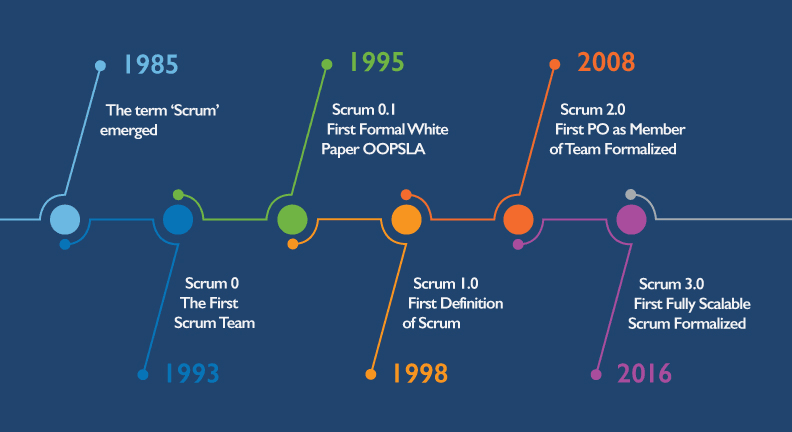
To stress the importance of teamwork to deal with a complex problem, in 1993, Jeff Sutherland implemented the first scrum project at the easel corporation.
After that, software developers Schwaber and Sutherland each came up with their version of Scrum, which they presented at a conference in Austin in 1995. Each Scrum has its roots in the technology and software industries.
Scrum was initially developed for managing and developing products. Currently, it is being used extensively worldwide across every industry.
Scrum is an evolution of Agile practices. Here we have pinpointed some points that you need to know about scrum:
The Scrum Team consists of the Product Owner, Scrum Master and Development Team. The people who fulfill these roles work together closely daily to ensure the smooth flow of information and the quick resolution of issues.
Let’s go through these three roles.
The Product Owner defines what the product will look like and what features it should contain. He or she keeps track of the project’s stakeholder’s expectations, defines and gathers the required tools and resources that the scrum team needs.
In addition, The product owner communicates the project vision to the team to help set priorities.
The tasks of a Product Owner include:
Scrum Master is the coach and gatekeeper of the scrum team. They must know Scrum and Agile Software Development.
They help the team perform at its highest level. Scrum Master does this by ensuring everyone in the group understands Scrum theory, practices, rules, and values.
The tasks of a Scrum Master include:
The Development Team consists of professionals who do the hands-on work of developing and testing the product owner put forth.
This team tends to be made up of several cross-disciplinary members. The Development Teams are structured and empowered by the organization to manage and organize their work.
The tasks of a Development Team include:
Scrum Artifacts are designed to maximize the transparency of essential information so that everybody has the same understanding of the artifact.
Let’s go through the Scrum Artifacts.
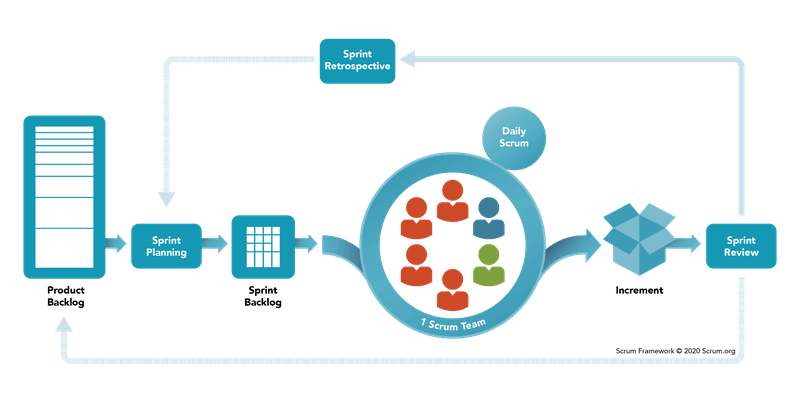
Product Backlog lists all features, functions, requirements, and fixes that constitute the changes to the product in future releases. It is constantly evolving and is never changing.
The product owner is responsible for the product backlog, including its content, availability, and ordering.
Sprint Backlog is the collection of product backlog items that the team commits to achieve in a given sprint.
The Sprint Backlog makes all the work that the development team identifies necessary to meet the sprint goal.
According to Scrum Guide, incremental is the sum of all the product backlog items completed during a sprint and the value of the increments of all previous sprints.
The increment must be in usable condition regardless of whether the product owner decides to release it.
Apart from these three, there is another one called Sprint Burndown Chart. It is a graphical way of showing how much work remains in the sprint, typically task hours. It is generally updated in the daily scrum.
Prescribed events are used in Scrum to create regularity and transparency in the organization. All events are time-boxed events which means that every event has a maximum duration.
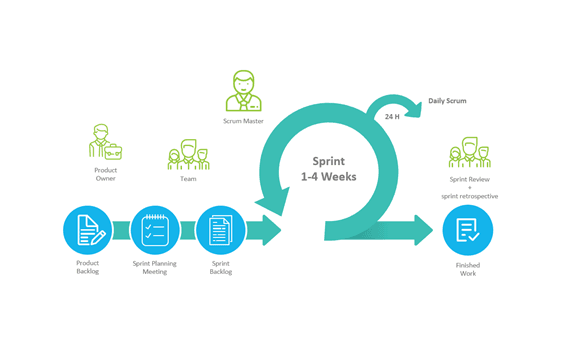
During the sprint planning meeting, the entire scrum team collaborates and discusses the work performed in the sprint. The scrum master ensures that the event takes place and attendants understand its purpose.
The meeting answers two questions:
The daily Scrum is a 15-minute time-boxed event for the development team. This meeting takes place every day during a sprint.
The development team uses the daily to assess its progress towards completing the work in the sprint backlog.
At the end of the sprint, a sprint review is held to inspect the product increment and update the product backlog if needed.
During the sprint review, the team and stakeholders collaborate about what was done in the sprint. Based on the feedback, they updated the product backlog.
The result of the sprint review is a revised product backlog that defines the probable product backlog items for the next sprint.
During the sprint retrospective, the team reflects upon how things went during the previous sprint and identifies adjustments they could make from now on.
It occurs after the sprint review and before the next sprint planning.
Scrum is based on a set of fundamental values. The values provide a code of behavior for scrum teams.
The five values are:
The three principles of Scrum are Transparency, Inspection, and Adaptation.
The team must work in an environment where everyone is aware of the problems that other team members are experiencing. Teams recognize issues that have been present for a long time and are obstructing the team's success.
The framework includes frequent inspection points to allow the team to reflect on how the process is working. The Daily Scrum meeting and the Sprint Review Meeting are two of these inspection points.
The team constantly investigates how things are progressing and revises any items that do not make sense.
Here’s a 6 step outline of how a scrum process works:
In Software project development, the development cycle encounters various uncertainties in resource allocation, cost optimization, and, most importantly, a sudden change in customer requirements.
Scrum is the solution that is designed to satisfy customers’ needs throughout the project’s development.
Here’s why you should consider Scrum for your project development:
By now, you already know how scrum can help you ace your project development. First, try to identify the needs of your business and assess how scrum can fit in your existing process.
PolyUno emphasizes tasks, project schedule, deliverables, and budget to meet customers’ expectations. If you’re looking for a customer-focused agency for software solutions, PolyUno would be the best choice for you.
So, What are you waiting for? Request a quote now!